Harvesting Warmth from the Cold: The Fascinating World of Heat Pumps
"We don’t need to generate heat; we just need to find it and move it." — This quote perfectly captures the essence of heat pump technology. A heat pump works by extracting heat from external sources, such as air, water, or underground soil, and transferring it indoors for heating or cooling. This process makes heat pumps highly efficient and energy-saving. In this article, we’ll explore the technology behind heat pumps through an interesting story, discuss the different types of heat pumps available, highlight their pros and cons, and guide you on how to choose the right one for your needs.
I.An Interesting Story About Heat Pumps
The concept of heat pumps dates back to the 19th century. In 1852, physicist William Thomson (later known as Lord Kelvin) proposed the idea that heat could be transferred from a cold place to a warmer one. Although this idea was introduced long ago, it wasn’t until the mid-20th century that heat pump technology began to gain widespread use.
Sweden was one of the first countries to apply heat pumps on a large scale. Given the harsh winters, Sweden needed more efficient heating solutions. In the 1960s, Swedish scientists successfully applied geothermal heat pump technology to residential heating systems, resulting in significant energy savings. Today, nearly every home in Sweden uses a heat pump for heating, making the country a global leader in heat pump adoption.
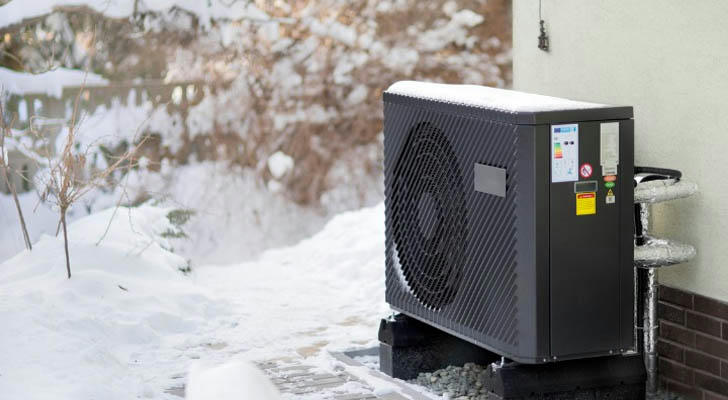

II.Types of Heat Pumps in the Market and Their Pros and Cons
Air Source Heat Pumps (ASHP)
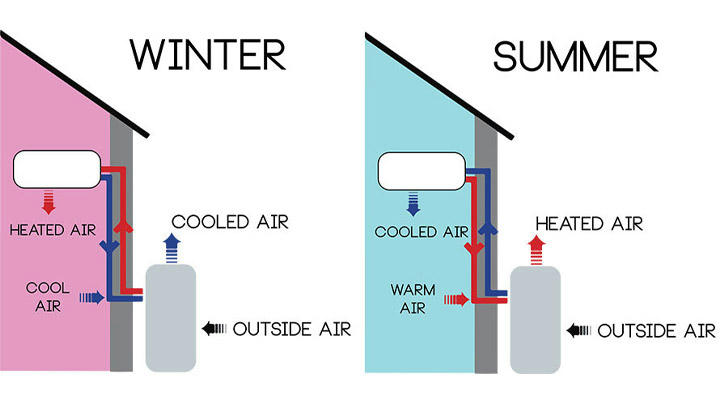
1.Pros: Easy to install, relatively low initial cost, and ideal for moderate climates. These pumps work by extracting heat from the outdoor air and transferring it indoors for heating or cooling.
2.Cons: Their efficiency decreases in extremely cold temperatures, and they may require additional heating during severe winter weather.
Ground Source Heat Pumps (GSHP)
1.Pros: Ground source heat pumps are highly efficient and are unaffected by temperature fluctuations, making them ideal for colder regions. They use the stable temperature of the ground to exchange heat, ensuring reliable performance.
2.Cons: These systems require a higher upfront investment due to the need for underground piping installation, which demands more space and excavation.
Water Source Heat Pumps (WSHP)
1.Pros: Water source heat pumps are highly efficient and perform well in areas with stable water sources, such as lakes, rivers, or groundwater. Since water temperature remains relatively constant, the system operates efficiently year-round.
2.Cons: These systems require access to a nearby water source, and installation can be complicated and expensive, particularly if the water source is far from the property.

III.How to Choose the Right Heat Pump
Climate: The local climate should be the first consideration when choosing a heat pump. In colder regions, ground source heat pumps are usually the best option due to their high efficiency and reliable performance in low temperatures. For milder climates, air source heat pumps are generally more suitable.
Energy Source: If you’re looking for an environmentally friendly option, consider heat pumps powered by renewable energy sources, such as solar panels. Some heat pump systems can even be integrated with solar energy, further reducing carbon emissions and lowering operating costs.
Installation Costs and Space Requirements: Ground source heat pumps require more space for installation because they need to be buried underground, which increases both installation complexity and upfront costs. On the other hand, air source heat pumps are easier to install and are more flexible, especially for properties with limited space.
Maintenance and Lifespan: Heat pumps typically have long lifespans, ranging from 15 to 20 years. It’s important to choose a reliable brand with a good reputation for customer service and regular maintenance. Regular maintenance will help ensure the system runs efficiently and extend its lifespan.
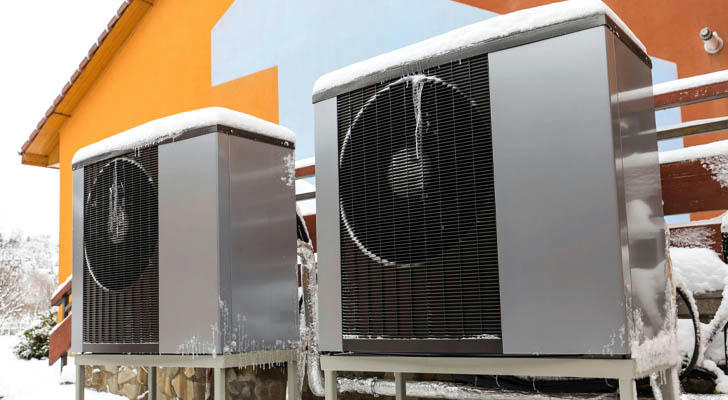

IV.Conclusion
Heat pumps are an energy-efficient and environmentally friendly solution for heating and cooling. By extracting heat from external sources and transferring it indoors, heat pumps reduce reliance on traditional heating and cooling systems, save energy, and reduce carbon emissions. While the initial investment can be higher than conventional systems, the long-term energy savings make heat pumps a smart investment for both homeowners and businesses.
As the world continues to shift toward greener, more sustainable energy solutions, heat pump technology will play an increasingly important role in reducing global carbon footprints. By choosing the right heat pump for your needs, you can ensure a comfortable indoor environment while also contributing to a cleaner, more energy-efficient future.
